Automated Guided Vehicles (AGV) are autonomous mobile robots that are designed to transport materials, products or goods without the need for human intervention. AGV has a rich history dating back to the 1950s when the first AGV was developed by Barrett Electronics of Northbrook, Illinois. Since then, AGV has undergone tremendous transformations, including technological advancements that have revolutionized industries. Today, AGV is a crucial component of logistics and manufacturing facilities used to enhance efficiency and productivity. Read More…
We invented the AGV in 1954 and offer the most affordable & versatile AGV capabilities. Our AGVs automatically transport pallets, racks, bins, totes, rolls, boxes, racks, etc. in all types of manufacturing and warehouse facilities. Our tape/target/structure-free, ‘virtual path’ navigation requires no floor path maintenance and does not use/require line-of-sight to often blocked building ...
America in Motion was founded in 2007 with a mission to bring customized automated vehicle designs and solutions to the masses. Serving customers in the fibers, paper, automotive, food, consumer products, heavy equipment, and general manufacturing. Our team specializes in fully customizable AGVs but also offers the option to build an automated vehicle by using a simplified modular approach (also...
With over 1700 mobile robotics deployed worldwide and with over 30 million miles accumulated, Oceaneering Mobile Robotics (OMR) delivers best-in-class solutions with the lowest total cost without sacrificing performance. For over 30 years, OMR has been a trusted partner of exclusive brands in the automotive, healthcare, manufacturing, and (intra-) logistics industries.
Invio Automation is a leading comprehensive AGV, AMR, and robotics integrator with 10 engineering and support sites throughout North America. We specialize in heavyweight and assembly line applications.
For over 30 years, companies have turned to RedViking for ways to increase throughput and minimize infrastructure. We are a leading AGV manufacturer, and our AGVs are efficient and user-friendly. Our AGV solutions are cleaner, more sustainable, and require less infrastructure than traditional conveyance methods. We can provide full custom design tooling for your AGV so it meets every requirement...
IDC Corporation produces a line of Automated Guided Carts (AGCs) for various industrial applications, including standard product line carts and custom-designed systems tailored to specific customer needs. The various models are built on a common control architecture that support various mechanical configurations, and support operations ranging from simple delivery loops to sophisticated...
More Automatic Guided Vehicles Manufacturers
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are sophisticated, self-driving machines designed to automate and optimize material handling processes in various industries. Understanding AGV components is crucial for evaluating, specifying, and selecting AGV solutions that maximize automation ROI. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the essential AGV parts and systems:
- Navigation System
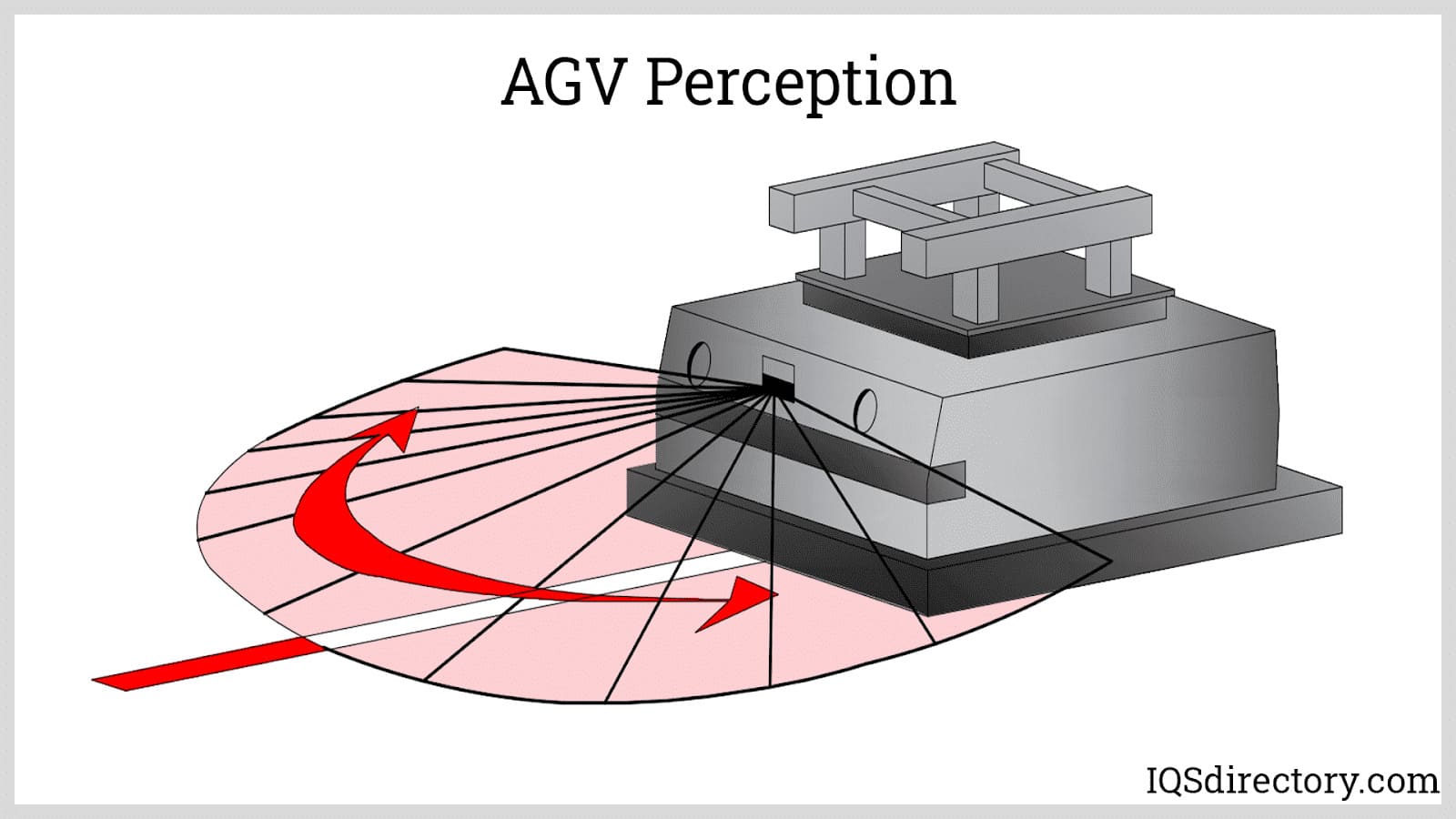
The navigation system is the AGV’s “brain,” enabling autonomous movement and route precision. It includes advanced sensors such as LIDAR, laser scanners, ultrasonic sensors, magnetic tape readers, and sometimes machine vision cameras. Modern AGVs often feature SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping), allowing real-time mapping, path planning, and localization. For example, Otto Motors’ warehouse bots use dynamic mapping to maneuver complex facilities. Choosing the right navigation technology is crucial for adapting to your facility’s layout and workflow. - Drive Unit
Electric motors (commonly DC or brushless) power AGV wheels or tracks. These motors, paired with high-efficiency gearboxes, deliver the necessary torque and speed for smooth operation. Differential steering, where two motors independently control wheel speed, enables tight maneuvering—ideal for narrow aisles or congested spaces, such as those encountered by JBT’s automated forklifts. The drive system affects AGV agility and operational efficiency. - Chassis/Frame
The chassis provides structural strength and durability, typically constructed from reinforced steel or lightweight aluminum. The frame design varies—tuggers, carts, forklifts, or custom solutions—based on payload requirements. Kiva Systems’ low-profile AGVs, for example, are optimized for under-rack navigation, while heavy-duty models can carry loads exceeding 10 tons. Durable casters and shock-absorbing mounts enhance stability and longevity. - Power Supply
AGVs are powered by rechargeable batteries—typically lithium-ion or lead-acid—supplying 24-48 volts for long shifts (8–12 hours). Fast-charging docks, battery swap systems, or inductive (wireless) charging pads ensure minimal downtime. Companies like Dematic have pioneered rapid battery-swapping for continuous operation. Battery selection impacts AGV uptime, lifecycle costs, and maintenance. - Control System
Onboard computers or programmable logic controllers (PLCs) execute navigation, obstacle avoidance, and route optimization algorithms. These systems process sensor input, communicate with central fleet management software, and interface with warehouse management systems (WMS) or manufacturing execution systems (MES). Wireless connectivity (Wi-Fi, RFID, or 5G) enables real-time status monitoring and dynamic task allocation. Software like Fetch Robotics’ platform optimizes routing and load balancing across fleets. - Load Handling Mechanism
AGVs are equipped with specialized attachments to move materials efficiently: forks for pallet lifting, conveyor tops for integration with assembly lines, rollers, clamps, or tow hitches for carts and trailers. The right load handling equipment ensures compatibility with your material flow—such as Toyota’s AGVs that automatically align with pallets or bins for hands-free loading. - Safety Features
Safety is paramount in AGV deployment. AGVs incorporate bumper sensors, emergency stop buttons, light curtains, audible alarms, and 360-degree obstacle detection using infrared or sonar sensors. State-of-the-art AGVs employ redundant safety layers to comply with global industrial safety standards (ISO 3691-4, ANSI/ITSDF B56.5). These features are vital for safe operation in environments shared with workers or other vehicles.
These integrated components enable AGVs to operate seamlessly in warehouses, factories, distribution centers, hospitals, and more. Understanding AGV construction helps buyers make informed decisions regarding automation technology selection, customization, and implementation.
Want to explore the best navigation systems for your facility? Request expert guidance from top AGV suppliers now.
Types of Automated Guided Vehicles
AGV technology has evolved to meet the growing demands of modern material handling, logistics, and manufacturing operations. There are several types of AGVs, each designed for specific use cases, environments, and payload requirements. Explore the most common AGV vehicle types and their applications below:
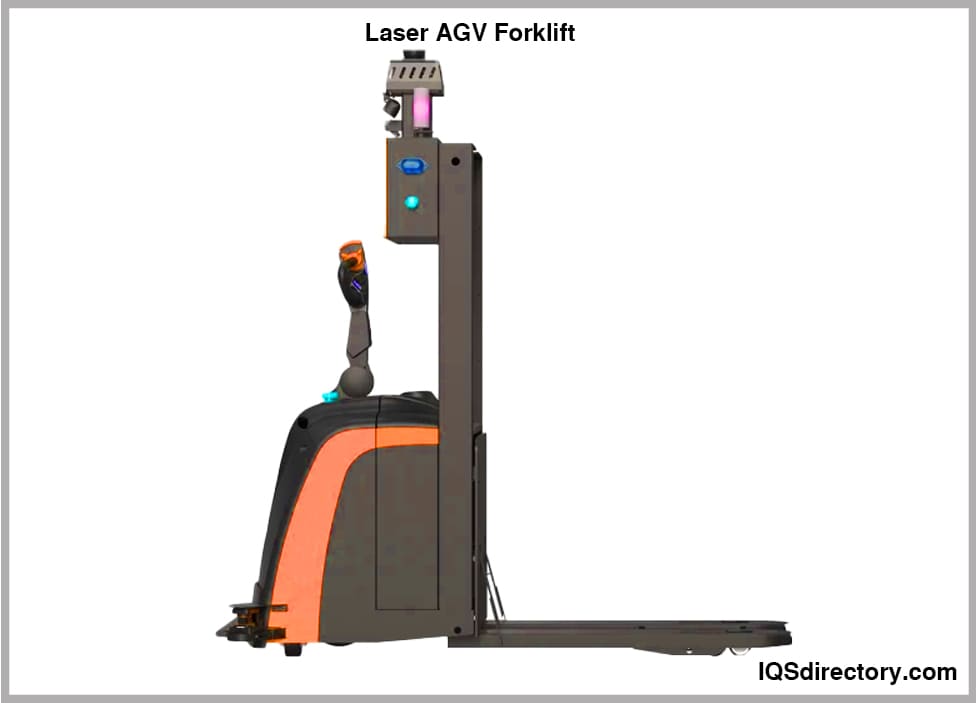
- Forklift AGVs are engineered to automate pallet handling and heavy lifting tasks in warehouses, distribution centers, and manufacturing plants. These AGVs replace traditional forklifts, featuring robust forks and lifting mechanisms for stacking, unstacking, and transporting pallets, crates, or large containers. Forklift AGVs are ideal for high-volume warehouses seeking to reduce labor costs and increase safety by minimizing human-operated forklift traffic.
- Tugger AGVs are designed to tow multiple carts, trailers, or trains of goods throughout a facility. Commonly deployed in automotive assembly plants, warehouses, and large-scale logistics hubs, tugger AGVs streamline the movement of raw materials, components, and finished products between workstations, inventory zones, and shipping docks. Their towing capacity, flexibility, and ability to follow complex routes make them indispensable for lean manufacturing and just-in-time (JIT) processes.
- Unit Load AGVs specialize in transporting entire pallets or large loads, often between storage areas, assembly lines, and shipping points. These AGVs are programmable to follow fixed or dynamic routes, using advanced sensors and onboard cameras to navigate congested or changing environments safely. Unit load AGVs are popular in facilities where repetitive, high-volume transfers are required, such as in food and beverage, pharmaceutical, and electronics industries.
- Assembly Line AGVs are tailored for supporting flexible, automated production lines. These vehicles deliver components, tools, or subassemblies to precise locations along the assembly line, synchronized with production schedules. They can be programmed for precise timing and sequencing, reducing bottlenecks and enhancing workflow continuity. Assembly line AGVs are widely used in automotive, electronics, and appliance manufacturing.
- Hospital AGVs are purpose-built for healthcare environments, where hygiene, safety, and reliability are top priorities. These AGVs autonomously transport medications, sterile supplies, medical records, and even meal trays between departments, freeing up clinical staff for patient care. Advanced navigation and obstacle avoidance ensure safe passage through busy corridors and elevators.
- Automated Guided Carts (AGCs) are compact, versatile AGVs designed for light- to medium-duty material transport within factories, warehouses, and distribution centers. AGCs follow magnetic tape, QR codes, or laser guidance to navigate predefined routes, making them ideal for shuttling parts, totes, or small batches between workstations. Their modularity and flexibility allow easy reconfiguration as workflows change.
Not sure which AGV type fits your operation? Compare AGV models and get personalized recommendations from leading manufacturers.
Limitations of AGV
While Automated Guided Vehicles provide numerous operational benefits, understanding their limitations is essential for effective deployment and expectation management:
- High Initial Investment: AGV implementation requires capital outlays for vehicle purchase, guidance infrastructure (magnetic tape, markers, or QR codes), software integration, and facility modifications. ROI is realized over time through labor savings and efficiency gains.
- Path Flexibility: Many AGVs still follow pre-programmed routes, limiting their ability to adapt to sudden layout changes or unexpected obstacles. Although navigation technologies are improving, true dynamic flexibility may require more advanced (and expensive) AI-driven systems.
- Limited Human-Like Decision-Making: AGVs excel at repetitive tasks but struggle with jobs requiring nuanced human judgment, such as improvising in unforeseen scenarios or handling fragile, irregular loads.
- Cybersecurity and Safety Risks: As networked devices, AGVs are susceptible to hacking or unauthorized access. Additionally, if safety sensors fail or are overridden, collisions with people or equipment can occur. Rigorous cybersecurity and safety protocols are essential.
- Dependency on Infrastructure: AGVs often depend on environmental markers, wireless networks, or facility layouts. Disruptions to these elements can halt operations or reduce efficiency.
Curious about mitigating AGV limitations in your facility? Consult with automation experts now.
Choosing the Proper AGV
Selecting the right Autonomous Guided Vehicle for your business involves a strategic evaluation of operational needs, technical requirements, and long-term goals. Follow these steps for a successful AGV procurement process:
Assess Your Needs and Requirements
- Define Use Cases: Identify specific material handling tasks—such as order picking, assembly support, inventory transport, or shipping—that AGVs will automate.
- Examine Facility Layout: Consider aisle widths, turning radii, floor conditions, and the presence of elevators, ramps, or hazardous zones. Map traffic flow and bottlenecks to ensure AGV compatibility.
- Determine Payloads: Calculate maximum load weights, dimensions, and special handling needs (e.g., fragile items, hazardous materials).
Consider Navigation and Guidance Systems
- Evaluate Navigation Technologies: Choose between magnetic tape, laser guidance, vision-based navigation, or hybrid systems. Advanced facilities may benefit from SLAM or AI-powered navigation for maximum adaptability.
- Integration Needs: Assess compatibility with existing warehouse management systems (WMS), enterprise resource planning (ERP), and other automation solutions.
Determine Mobility and Power Requirements
- Drive Options: Differential drive excels in tight spaces; omnidirectional and tracked drives offer enhanced maneuverability for complex paths or uneven terrain.
- Battery Life and Charging: Assess operational runtime, charging methods (manual swap, auto-docking, or wireless), and battery health monitoring. Plan for charging infrastructure to reduce downtime.
- Load Capacity: Ensure the chosen AGV accommodates your maximum payloads safely, supporting future volume growth.
Analyze Integration and Scalability
- System Compatibility: Ensure seamless AGV integration with existing equipment, conveyor systems, racking, and control software to avoid operational disruptions.
- Fleet Expansion: Evaluate the vendor’s ability to scale your system—can additional AGVs be added without major reconfiguration?
- Workflow Adaptability: Choose AGVs that can be reprogrammed or upgraded to accommodate new processes as your business evolves.
Evaluate Cost and Return on Investment
- Total Cost of Ownership: Include hardware, software, installation, facility modifications, training, and ongoing maintenance in your cost analysis.
- ROI Calculation: Weigh expected efficiency gains, labor cost reductions, improved safety, and error reduction against upfront and recurring expenses.
- Lifecycle Support: Consider vendor-provided support, spare parts availability, and warranty terms to minimize long-term risks.
Vendor Selection: Additional Areas to Research and Compare
- Reputation and Reliability: Research customer reviews and case studies to assess vendor experience in your industry.
- Technical Support: Evaluate after-sales service, training programs, and remote troubleshooting capabilities.
- Customization: Ensure the vendor can tailor AGVs to your operational needs, including payloads, guidance systems, and software integration.
Ready to compare AGV vendors? Submit an RFQ to contact multiple AGV suppliers at once.
Benefits of AGV
Autonomous guided vehicles are revolutionizing material handling and logistics by delivering measurable benefits that drive competitive advantage. Here’s how AGVs can transform your operation:
- Enhanced Efficiency: AGVs automate repetitive transport, picking, and delivery tasks, enabling continuous 24/7 operations. Automated routing algorithms reduce travel distances and idle time, accelerating order fulfillment and reducing operational bottlenecks.
- Workplace Safety: Built-in sensors and safety controls prevent collisions, safeguarding employees and equipment. By reducing the need for manual forklifts or carts, AGVs minimize workplace accidents and ergonomic injuries.
- Space Optimization: AGVs navigate tight spaces, narrow aisles, and high-density storage layouts with precision. This allows for more efficient use of warehouse floor space and supports high-density storage designs.
- Operational Flexibility: AGVs can be reprogrammed for new tasks or routes as business needs change. Their modularity supports process reengineering and workflow optimization, making businesses more agile and responsive.
- Real-Time Data Insights: AGVs collect and transmit operational data—such as location, inventory status, and equipment health—to management systems. This transparency enables predictive maintenance, inventory optimization, and data-driven decision-making.
- Cost Reduction: AGVs reduce labor dependency and associated costs (wages, training, insurance). Lower maintenance requirements compared to combustion-powered vehicles further decrease total cost of ownership. Efficient battery management also contributes to energy savings.
- Environmental Sustainability: Electric AGVs operate with zero direct emissions, supporting green initiatives and regulatory compliance. By replacing diesel or gas-powered vehicles, AGVs help companies achieve sustainability targets and reduce their carbon footprint.
Wondering how AGVs could benefit your facility? Request a personalized AGV ROI analysis from top vendors.
What are the Applications of Automated Guided Vehicles?
Answer:
Automated Guided Vehicles are transforming a variety of industries by automating material movement, boosting productivity, and enhancing accuracy. Key AGV use cases include:
- Warehousing and Distribution: In e-commerce fulfillment centers, AGVs (like Amazon’s Kiva robots) transport goods between storage locations and packaging stations, dramatically shortening picking times and supporting fast order processing. AGVs optimize logistics for 24/7 operation, reducing dependency on manual labor.
- Manufacturing: AGVs transport raw materials, subassemblies, and finished goods within factories, synchronizing with just-in-time production systems. For example, Toyota’s tugger AGVs keep assembly lines supplied, minimizing inventory and labor costs.
- Automotive Industry: Heavy-duty AGVs move engines, chassis, and other large components between production cells. Automated forklifts and unit load AGVs improve safety and throughput in high-volume automotive plants.
- Healthcare: Hospitals deploy AGVs to deliver medications, linens, sterile supplies, and meals, enhancing workflow efficiency and freeing staff to focus on patient care. Swisslog’s TransCar AGVs are a leading example of medical AGV applications.
- Food and Beverage: AGVs automate the handling of ingredients, packaging, and finished products. In cold storage or temperature-controlled environments, AGVs (e.g., those used by PepsiCo) ensure safe, hygienic, and efficient movement of goods.
- Aerospace: AGVs transport large, delicate components such as wing panels and fuselage sections within assembly hangars, reducing the risk of damage and supporting lean manufacturing.
- Retail and E-commerce: AGVs support in-store inventory management, restocking, and real-time shelf monitoring. Robots like Bossa Nova scan shelves and update inventory systems, enabling accurate fulfillment and reducing out-of-stocks.
AGVs are also used in pharmaceuticals, electronics, chemicals, and general goods distribution, automating any repetitive, high-volume material movement task. Their adaptability—towing, lifting, or carrying—makes them suitable for both standard and highly specialized applications.
Searching for AGV solutions tailored to your industry? Connect with industry-specific AGV suppliers today.
The Future and AGVs
The future of AGVs is shaped by rapid advances in robotics, artificial intelligence, and industrial connectivity. Autonomous guided vehicles are expected to become even more intelligent, flexible, and seamlessly integrated into the smart factories, warehouses, and hospitals of tomorrow.
Emerging Trends:
- AI-Driven Navigation: Next-generation AGVs will leverage artificial intelligence for real-time decision-making, dynamic obstacle avoidance, and adaptive route planning. Machine learning and computer vision will enable AGVs to navigate unpredictable environments and optimize workflow automatically.
- IoT and Industry 4.0 Integration: AGVs are increasingly connected to enterprise systems via IoT, sharing data with robots, machines, and digital twins for synchronized, end-to-end process automation. This connectivity enables predictive maintenance, remote monitoring, and fleet optimization.
- Advanced Battery Technology: Future AGVs will feature longer-lasting, faster-charging batteries—such as solid-state or supercapacitors—enabling round-the-clock operation and reduced maintenance.
- Customizable Platforms: Modular AGV designs will allow businesses to tailor vehicles for specific payloads, environments, and applications, reducing the need for “one-size-fits-all” solutions.
- Expanded Applications: As reliability and intelligence increase, AGVs will move beyond logistics into service industries, agriculture, construction, and even public spaces.
With these advancements, AGVs are set to revolutionize industrial automation, offering unmatched productivity, safety, and operational insight.
Want to stay ahead of AGV trends? Discuss future-ready AGV options with expert providers.
How will AI affect the future of Automated Guided Vehicles?
Answer:
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing AGV capabilities, taking automation to unprecedented levels. Here’s how AI is shaping the next generation of AGVs:
- Dynamic Navigation: AI-powered AGVs use deep learning, LIDAR, and real-time sensor fusion to map and interpret dynamic environments. Unlike traditional AGVs constrained by fixed paths, AI-driven models (like Seegrid’s) autonomously adapt to floor layout changes, reroute around obstacles, and recover from disruptions without human intervention.
- Predictive Optimization: AI analyzes data from AGV sensors—battery status, load weight, facility traffic—to optimize routes, minimize congestion, and manage fleet scheduling. Predictive maintenance algorithms forecast wear and tear, reducing downtime and extending vehicle life.
- Task Versatility: With computer vision and reinforcement learning, AI enables a single AGV to perform multiple tasks—switching from pallet picking to bin delivery on demand. This flexibility is valuable in industries facing fluctuating demand or complex workflows.
- Human-Robot Collaboration: AI-powered “cobot” AGVs learn from operators, adapting to new workflows and environments. Enhanced safety analytics process sensor data in real time, enabling AGVs to preemptively halt or adjust paths to avoid collisions.
- Cost and Security Considerations: Advanced AI features increase up-front costs and require robust cybersecurity defenses, given increased connectivity and data sensitivity. Nonetheless, the productivity, safety, and scalability benefits are expected to drive widespread adoption—industry analysts project that AI-enhanced AGVs could dominate the market by 2030.
Interested in AI-powered AGVs? Explore smart automation options with top providers.
Choosing the Right AGV Company
For optimal results in purchasing AGV equipment, it’s essential to compare multiple AGV companies and solution providers. Our comprehensive directory features detailed company profiles, highlighting expertise, application specialties, and technology capabilities. Each listing includes direct contact options and a patented website previewer for a quick overview.
- Compare Multiple Vendors: Review company backgrounds, industry focus, and customer testimonials to identify the best fit for your project.
- Request Multiple Quotes: Use a single RFQ form to contact several AGV suppliers at once, streamlining your vendor selection process.
- Evaluate Support and Customization: Assess each vendor’s technical support, training, system customization, and after-sales service for a smooth implementation and long-term success.
Leverage our resources to accelerate your AGV buying process and ensure you partner with an automation provider who meets your operational and strategic goals.
For related automation solutions, check out our Parts Washers website.





 AGVs
AGVs Casters
Casters Cranes
Cranes Conveyors
Conveyors Electric Hoists
Electric Hoists Forklifts
Forklifts Hydraulic Lifts
Hydraulic Lifts Platform Lifts
Platform Lifts AGV
AGV Air Pollution Control
Air Pollution Control Assembly Machinery
Assembly Machinery Blowers
Blowers Conveyors
Conveyors Cranes
Cranes Deburring Machinery
Deburring Machinery Dust Collectors
Dust Collectors Heaters
Heaters Hose Reels
Hose Reels Lubricators
Lubricators Mezzanines
Mezzanines Modular Buildings
Modular Buildings Storage Racks
Storage Racks Ultrasonic Cleaners
Ultrasonic Cleaners Work Benches
Work Benches