An AGV system employs a self-guided or automated guided vehicle (AGV) to deliver raw materials or other required items to various points as part of a material-handling system. These systems are found in warehouses, distribution centers, and manufacturing plants to deliver parts and materials to workers at various stages of a manufacturing process through vehicles that do not require an onboard operator. These vehicles may also perform other functions like delivering incoming stock and materials directly to established storage sites within a facility. Read More…
We invented the AGV in 1954 and offer the most affordable & versatile AGV capabilities. Our AGVs automatically transport pallets, racks, bins, totes, rolls, boxes, racks, etc. in all types of manufacturing and warehouse facilities. Our tape/target/structure-free, ‘virtual path’ navigation requires no floor path maintenance and does not use/require line-of-sight to often blocked building ...
America in Motion was founded in 2007 with a mission to bring customized automated vehicle designs and solutions to the masses. Serving customers in the fibers, paper, automotive, food, consumer products, heavy equipment, and general manufacturing. Our team specializes in fully customizable AGVs but also offers the option to build an automated vehicle by using a simplified modular approach (also...
With over 1700 mobile robotics deployed worldwide and with over 30 million miles accumulated, Oceaneering Mobile Robotics (OMR) delivers best-in-class solutions with the lowest total cost without sacrificing performance. For over 30 years, OMR has been a trusted partner of exclusive brands in the automotive, healthcare, manufacturing, and (intra-) logistics industries.
Invio Automation is a leading comprehensive AGV, AMR, and robotics integrator with 10 engineering and support sites throughout North America. We specialize in heavyweight and assembly line applications.
For over 30 years, companies have turned to RedViking for ways to increase throughput and minimize infrastructure. We are a leading AGV manufacturer, and our AGVs are efficient and user-friendly. Our AGV solutions are cleaner, more sustainable, and require less infrastructure than traditional conveyance methods. We can provide full custom design tooling for your AGV so it meets every requirement...
IDC Corporation produces a line of Automated Guided Carts (AGCs) for various industrial applications, including standard product line carts and custom-designed systems tailored to specific customer needs. The various models are built on a common control architecture that support various mechanical configurations, and support operations ranging from simple delivery loops to sophisticated...
More AGV System Manufacturers
AGV System Designs
Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV) systems are at the forefront of modern material handling and intralogistics automation. These advanced, driverless transport systems are engineered to streamline internal transport, warehouse automation, and supply chain management across diverse industries. When evaluating AGV system designs, it’s vital to consider the broad spectrum of configurations, load capacities, and technological integrations that support various industrial applications and manufacturing environments.
AGV systems are available in a range of sizes and payload capacities to accommodate multiple use cases. From compact, light-load AGVs that efficiently move small components for electronics assembly, to heavy-duty automated guided vehicles capable of transporting cargo loads up to 250,000 pounds, the flexibility of AGV solutions is unmatched. These robust AGVs use features like wide platforms, reinforced chassis, and solid wheels to ensure safe and efficient material handling in demanding environments such as automotive plants, distribution centers, and aerospace manufacturing.
Between these extremes, you’ll find a variety of guided vehicle types, including tow tractors (draggers), forked AGVs, transfer shuttles, and automated pallet trucks. Each AGV vehicle type is optimized for specific logistics processes, such as:
- Tow Tractors: Efficiently transporting multiple trailers or carts in a train, ideal for just-in-time (JIT) production lines.
- Forked AGVs: Automated pallet stacking, racking, and retrieval in warehouse storage systems.
- Transfer Vehicles: Seamless point-to-point movement between production cells.
- Pallet Trucks: Moving bulky, oversized, or awkwardly shaped freight that manual labor cannot easily handle.
- AGV Carts: Simultaneous movement of multiple tons of goods between processing and storage areas.
Modern AGV fleets can be deployed to supplement human workers, optimize supply chain operations, or fully automate material flows in smart factories. Cargo-handling robots and AGVs are central to Industry 4.0 initiatives, enabling data-driven production, real-time inventory tracking, and integration with warehouse management systems (WMS) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) software.
Industry Applications of AGV Systems
AGV systems are implemented in a wide array of sectors, including:
- Automotive Manufacturing: Automated transport of car bodies, engines, and components between assembly stations.
- Food & Beverage: Hygienic, non-contact movement of raw materials, packaging, and finished goods.
- Pharmaceuticals: Secure, traceable delivery of sensitive or hazardous materials within cleanroom environments.
- Logistics & Distribution: Automated loading and unloading, cross-docking, and order fulfillment.
- Electronics: Precise, gentle handling of delicate parts and subassemblies.
- Aerospace: Heavy load handling, work-in-progress (WIP) transport, and final product movement.
Benefits of AGV System Integration
Curious about the advantages of AGV technology for your facility? Explore these key benefits:
- Labor Cost Reduction: AGV solutions automate repetitive, time-consuming tasks, allowing your workforce to focus on higher-value activities.
- Increased Safety: Advanced obstacle detection, collision avoidance, and fail-safe protocols reduce workplace accidents and injuries.
- Consistent Throughput: AGVs deliver predictable, round-the-clock performance, eliminating production bottlenecks and downtime.
- Scalability: Easily deploy additional AGVs to accommodate growth, seasonal demand, or new production lines.
- Data-Driven Optimization: Integration with digital logistics platforms enables real-time monitoring and continuous process improvement.
- Reduced Product Damage: Automated handling minimizes human error and mishandling of sensitive or valuable goods.
Comparing AGV Types: Which Solution Is Right for You?
Not sure which AGV system fits your operational needs? Consider these common decision factors:
- Required payload capacity and load dimensions
- Facility layout and route complexity
- Integration with existing equipment and IT infrastructure
- Navigation technology preferences (fixed path, laser-guided, natural feature, SLAM)
- Desired automation level (partial vs. full automation)
- Environmental conditions (temperature, cleanliness, floor quality)
Ask yourself: How can AGV systems improve productivity, lower operational costs, and future-proof my facility? For detailed guidance, explore our comprehensive AGV selection resources.
AGV Principle of Operation
The core principle behind every AGV system is autonomous navigation — enabling driverless vehicles to move materials safely and efficiently within defined workspaces. AGV operation relies on a combination of onboard sensors, smart navigation algorithms, and centralized fleet management software to ensure precise, reliable, and coordinated transport.
There are two primary navigation strategies utilized in AGV operations:
- Fixed Route Navigation: AGVs follow preconfigured paths, which are physically marked by embedded wires, magnetic tape, or colored paint/tape. These fixed-path AGV systems use onboard sensors, antennae, and RF (radio frequency) communication to stay on course. Although highly reliable for repetitive tasks, their inflexibility and inability to adapt to layout changes make them less popular for dynamic environments or facilities with frequent workflow adjustments.
- Free-Range (Dynamic) Navigation: In contrast, free-range AGVs leverage advanced internal navigation systems, such as lasers, LiDAR, or vision sensors, to autonomously detect obstacles, avoid collisions, and dynamically optimize routes. These systems are highly adaptable, making them ideal for complex, high-mix manufacturing or logistics centers where flexibility is critical.
With the evolution of AGV technology, modern fleets often utilize a mix of both navigation types, allowing facility managers to tailor solutions to specific operational requirements. For instance, a warehouse may deploy fixed-path AGVs for repetitive long-haul transport, while using free-range AGVs for flexible picking or replenishment tasks.
Interested in which AGV navigation approach best suits your facility? Compare fixed-path versus dynamic navigation systems based on your workflow, safety requirements, and long-term scalability.


Navigation Systems
Navigation technology is the heart of every AGV system. The choice of navigation method determines the AGV’s flexibility, accuracy, and suitability for specific industrial scenarios. Below, we explore the most widely used AGV navigation technologies:
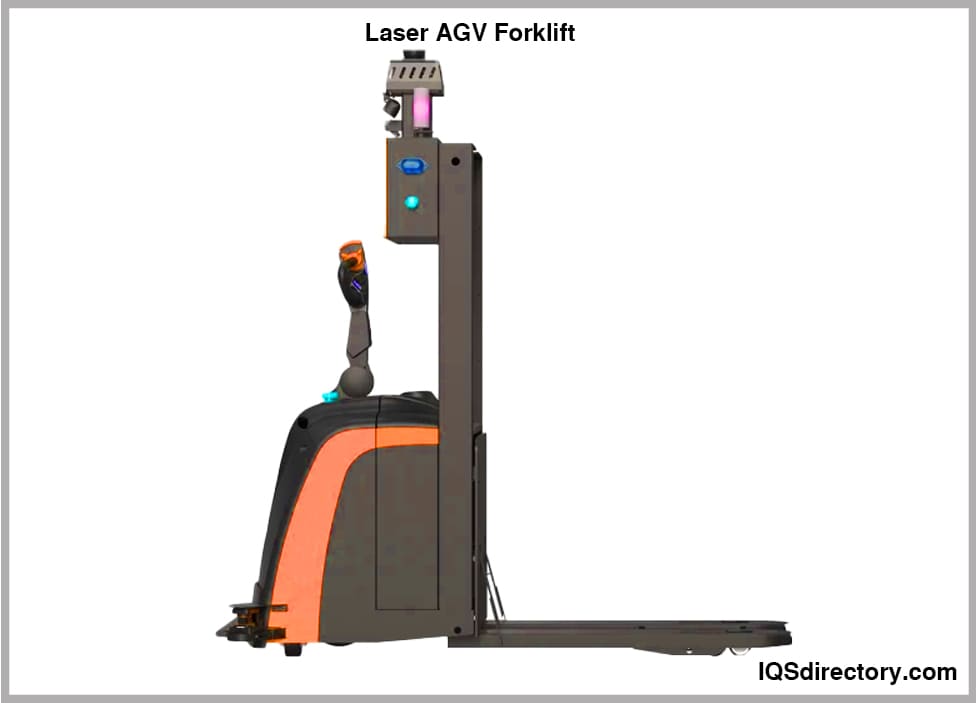
Laser Guided Navigation
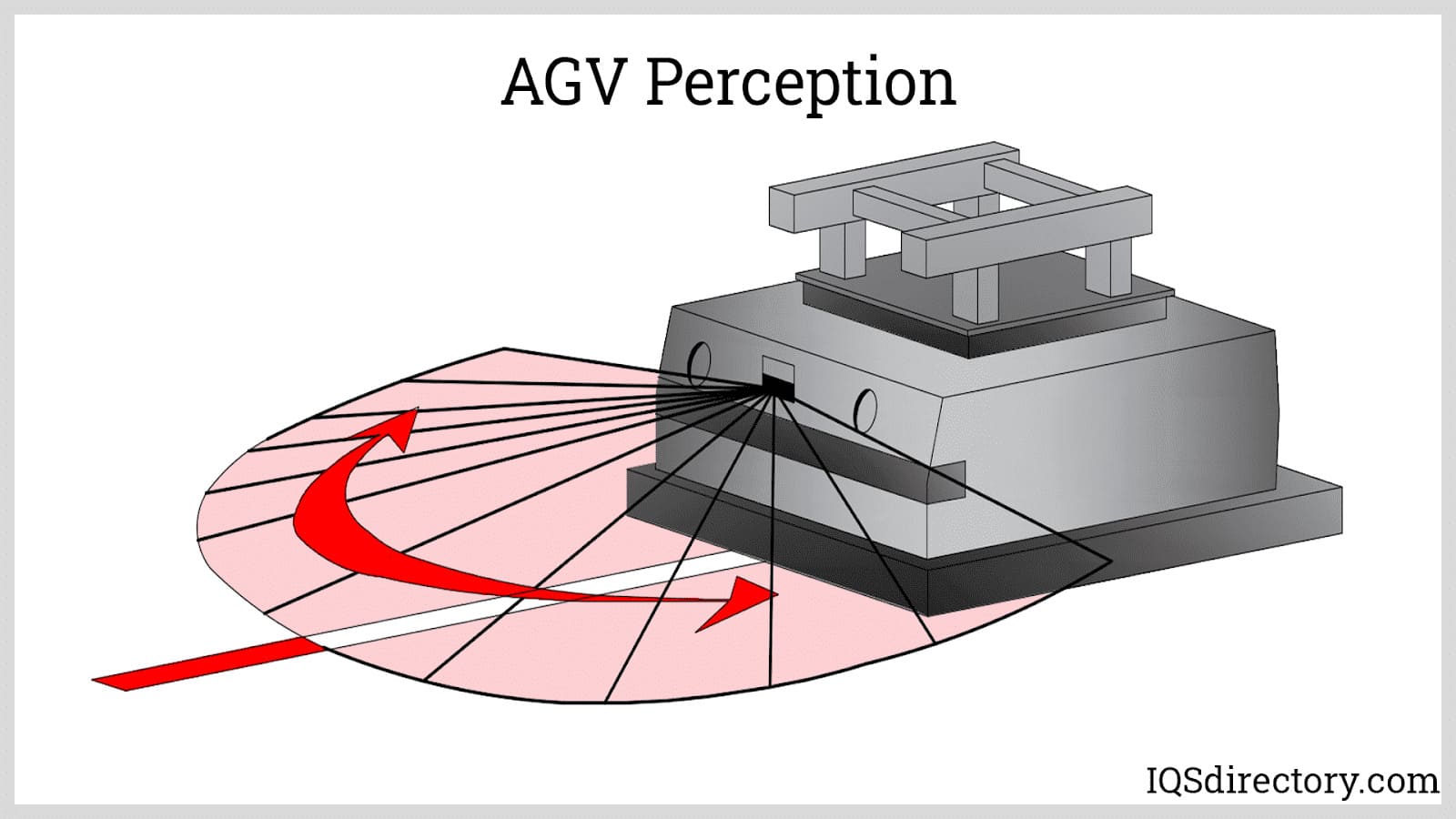
Laser Guided Vehicles (LGVs) are among the most popular types of automated guided vehicles for applications demanding high positional accuracy and flexible routing. In a typical LGV configuration, a precision laser navigation device is mounted atop a pole on the vehicle. This navigation system communicates with strategically placed reflectors (reflective tapes or cylinders) within the AGV’s operational environment, such as on columns, walls, or support poles.
The laser navigation device emits a continuous 360-degree array of laser beams, which bounce off reflectors and return to the system. By measuring the time and angle of each return signal, the LGV applies complex algorithms to triangulate its exact position, orientation, and heading within the mapped facility. Most LGVs require at least three reflectors in view to enable real-time positional calculations. Depending on the manufacturer and configuration, an LGV can update its position as frequently as 30–40 times per second, delivering exceptional repeatability and reliability for high-throughput logistics and assembly lines.
Laser-guided navigation is ideal for facilities where:
- Frequent layout changes are anticipated (the system can be easily reprogrammed for new reflector placements)
- High-precision movements are essential (such as in automated storage and retrieval systems)
- Complex route flexibility is required

SLAM Navigation
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) navigation is the most advanced and versatile method for AGV positioning. SLAM-based AGVs use an array of onboard sensors — including LiDAR, vision cameras, ultrasonic sensors, and inertial measurement units (IMUs) — to build a dynamic map of their environment while simultaneously calculating their precise location within it. This approach allows AGVs to operate in unstructured or changing environments, making them ideal for modern, flexible manufacturing and logistics facilities.
During initial setup, an operator may drive the AGV manually (using a handheld controller or gamepad) along desired routes. As the AGV moves, its sensors continuously scan and record environmental features, creating a digital map. This reference map is stored in the AGV’s control system, and can be enhanced with facility layout data from programs like AutoCAD. When in autonomous operation, the AGV continually compares its real-time sensor input with the stored map, allowing it to localize itself, follow optimal routes, and detect any changes or obstacles in its path.
SLAM navigation offers several compelling advantages:
- Works in environments without fixed infrastructure (such as warehouses with frequently shifting inventory)
- Enables easy reconfiguration of routes and workflows
- Provides robust obstacle detection and dynamic path planning
- Supports integration with other automation technologies, such as collaborative robots (cobots) and AMRs (autonomous mobile robots)
- Delivers exceptional accuracy by fusing odometry, encoder data, and environmental sensing

Other AGV Navigation Technologies
While laser-guided and SLAM navigation dominate high-tech AGV deployments, there are additional navigation methods to consider:
- Magnetic Tape or Wire Guidance: Cost-effective for simple, repetitive routes. Magnetic sensors on the AGV follow a tape or wire embedded in the floor.
- Optical Guidance: AGVs use vision sensors to follow painted or taped lines on the floor.
- RFID-Based Navigation: RFID tags placed along the route trigger specific actions or routing decisions.
- Natural Feature Navigation: AGVs use vision or LiDAR to recognize and localize based on permanent facility features, supporting highly flexible and infrastructure-light deployments.
Want to compare navigation technologies side by side? Contact our AGV specialists for a custom consultation based on your facility’s unique requirements.
How to Select the Best AGV System for Your Business
Choosing the right AGV system supplier is a critical step in ensuring a successful automation project. In a rapidly evolving marketplace, decision-makers must evaluate suppliers based on their technology portfolio, industry expertise, integration capabilities, and post-implementation support.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to selecting an AGV partner:
- Define Your Requirements: Analyze your facility layout, workflows, load types, throughput goals, and integration needs. Consider the level of autonomy, navigation technology, and software compatibility you require.
- Research AGV Manufacturers: Use our curated list of AGV system companies to compare at least five qualified vendors. Review each supplier’s business profile, technology focus, and successful case studies.
- Evaluate Solutions: Assess the AGV models offered (tow tractors, forked AGVs, pallet trucks, mobile robots, etc.), supported navigation systems, and integration with your warehouse management, ERP, or manufacturing execution systems.
- Request Information and Quotes: Use the provided contact forms to reach out directly for more details, technical specifications, or to request a tailored quote. Leverage our website previewer to quickly understand each company’s unique strengths.
- Arrange Demonstrations: Schedule site visits or virtual demos to see AGV systems in action and assess usability, scalability, and support services.
- Check References and Support: Ask for references from similar installations and inquire about training, spare parts availability, and long-term maintenance services.
When comparing AGV vendors, ask yourself:
- Does the supplier’s technology align with our current and future automation goals?
- How responsive and knowledgeable is their support team?
- Can their AGV solutions scale with our business as volumes and requirements change?
- What integration services and post-sale support do they offer?
For additional guidance, consult our AGV supplier directory and leverage our RFQ form to contact multiple AGV businesses simultaneously. This approach streamlines your evaluation process and ensures you find the best fit for your logistics automation needs.
Frequently Asked Questions About AGV Systems
- What is the difference between AGVs and AMRs?
AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles) typically follow fixed or semi-fixed paths using defined navigation aids. AMRs (Autonomous Mobile Robots) use onboard intelligence and environmental sensing to navigate freely in dynamic environments, making them more flexible for complex applications. - How do I justify the ROI of AGV implementation?
Calculate cost savings from labor reductions, increased throughput, improved safety, and decreased product damage. Factor in long-term scalability and digital transformation benefits. - Are AGV systems safe to operate alongside human workers?
Yes. Modern AGV systems are equipped with advanced safety features, including obstacle detection, speed monitoring, and emergency stop functions, ensuring safe coexistence with personnel. - What types of facilities benefit most from AGV systems?
AGVs are ideal for manufacturing plants, warehouses, distribution centers, hospitals, and any environment requiring repetitive, predictable material transport. - Can AGVs be retrofitted into existing facilities?
Absolutely. Many AGV systems are designed for easy integration with minimal infrastructure changes, allowing businesses to automate material flows without extensive remodeling.
Choosing the Correct AGV Systems Supplier
To make sure you have the most productive outcome when purchasing AGV Systems from an AGV Systems Supplier, it is important to compare at least 5 Manufacturers using our list of AGV Systems companies. Each AGV Systems Supplier has a business profile page that highlights their areas of experience and capabilities and a contact form to directly communicate with the manufacturer for more information or request a quote. Review each AGV Systems company website using our patented website previewer to get an idea of what each business specializes in, and then use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple AGV Systems businesses with the same form.
Ready to start your AGV project? Explore top AGV system suppliers or contact our AGV experts for a personalized consultation.





 AGVs
AGVs Casters
Casters Cranes
Cranes Conveyors
Conveyors Electric Hoists
Electric Hoists Forklifts
Forklifts Hydraulic Lifts
Hydraulic Lifts Platform Lifts
Platform Lifts AGV
AGV Air Pollution Control
Air Pollution Control Assembly Machinery
Assembly Machinery Blowers
Blowers Conveyors
Conveyors Cranes
Cranes Deburring Machinery
Deburring Machinery Dust Collectors
Dust Collectors Heaters
Heaters Hose Reels
Hose Reels Lubricators
Lubricators Mezzanines
Mezzanines Modular Buildings
Modular Buildings Storage Racks
Storage Racks Ultrasonic Cleaners
Ultrasonic Cleaners Work Benches
Work Benches